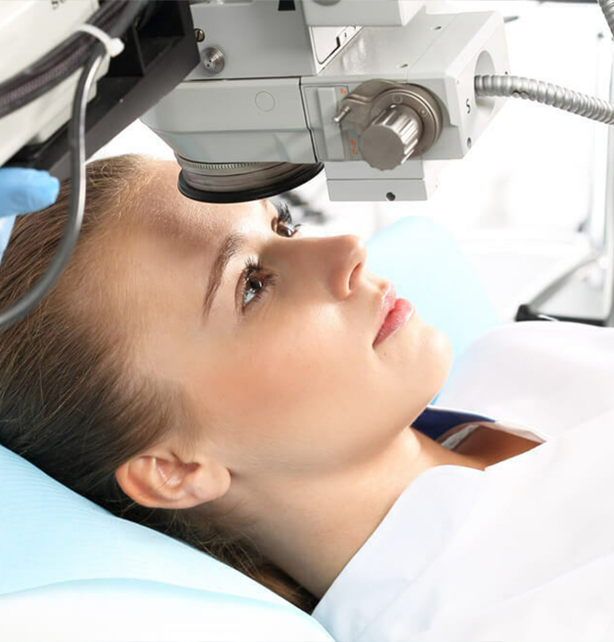
Laser Eye Surgeries: Focus on LASIK
Laser eye surgeries, such as LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis), have revolutionized the field of ophthalmology by providing a safe and effective way to correct refractive errors, including nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. In this article, we’ll dive into the world of laser eye surgeries, with a special focus on LASIK.
What is LASIK?
LASIK is a type of refractive surgery that uses a laser to reshape the cornea, improving the eye’s focusing power. By altering the shape of the cornea, LASIK can help reduce or eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses.
How Does LASIK Work?
- The surgeon creates a thin, hinged flap in the cornea using a femtosecond laser or a microkeratome blade.
- The flap is gently lifted, allowing access to the inner corneal tissue.
- An excimer laser is used to remove microscopic amounts of tissue and reshape the cornea according to the patient’s specific refractive error.
- The flap is then repositioned, and it will heal naturally without stitches.
Candidacy for LASIK
To be a good candidate for LASIK, you should:
- Be at least 18 years old
- Have a stable prescription for at least one year
- Have sufficient corneal thickness
- Not have certain eye conditions, such as severe dry eye or cataracts
- Not be pregnant or nursing
Benefits of LASIK
- High success rate in improving vision
- Minimal discomfort during and after the procedure
- Quick recovery time
- Long-lasting results
- Reduced or eliminated need for glasses or contacts
Risks and Side Effects
As with any surgical procedure, LASIK carries some risks and potential side effects, including:
- Dry eyes
- Glare, halos, or double vision
- Over- or under-correction
- Flap complications
- Vision loss (rare)
Other Laser Eye Surgeries
In addition to LASIK, there are other laser eye surgeries that your ophthalmologist may recommend depending on your specific needs:
- PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy): Similar to LASIK, but without the creation of a corneal flap. The surgeon removes the outer layer of the cornea before reshaping it with the excimer laser.
- SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction): A newer procedure that involves using a femtosecond laser to create a small, lens-shaped piece of tissue (lenticule) within the cornea, which is then removed through a small incision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long does LASIK surgery take?
A: The actual LASIK procedure typically takes less than 30 minutes for both eyes.
Q: Is LASIK painful?
A: Most patients experience little to no discomfort during the procedure. Some may feel slight pressure or experience mild discomfort for a short time after the surgery.
Q: How long does it take to recover from LASIK?
A: Most patients can return to normal activities within 24-48 hours after the procedure. However, complete visual recovery may take several weeks.
If you’re considering laser eye surgery, consult with your ophthalmologist to determine if you’re a good candidate and which procedure may be best suited for your needs. They can provide you with a comprehensive evaluation and discuss the potential benefits and risks involved.